LiDAR drones are changing the landscape of multiple industries. They combine advanced technology with practical applications. The fusion of LiDAR in drones is driving its significant economic impact across various sectors.
LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, employs laser pulses to capture highly accurate distance measurements, enabling the creation of detailed maps and realistic 3D models.
Industries like agriculture, construction, and mining are reaping the benefits of LiDAR drone survey. LiDAR drones offer enhanced data collection, improving efficiency and reducing costs. They also promote safety by minimising human involvement in risky environments.
The demand for LiDAR-equipped drones is growing. As technology advances, its applications continue to expand, promising a bright future for industries worldwide.
What is LiDAR Technology? Understanding the Basics
LiDAR technology utilises laser beams to measure distances. It analyses the time taken for the light to bounce back. This allows for precise distance measurements.
This technology generates high-resolution maps and 3D models. It’s invaluable for applications where accuracy is key. From mapping terrain to assessing structural integrity, LiDAR is indispensable.
There are several core components to a LiDAR system:
Laser: Emits pulses of light.
Scanner and Optics: Direct the laser beams.
Receiver Sensor: Captures the reflected light.
GPS: Provides position data for geo-referencing.
Light detection and ranging has diverse applications. It’s used in autonomous vehicles, agriculture, forestry, and more. The versatility of LiDAR technology continues to grow.

Understanding “LiDAR Technology” is crucial for grasping its potential. As it integrates with drones, its impact on industries becomes even more profound.
How LiDAR Drones Work: Key Components and Systems
LiDAR drones combine the powers of aerial platforms and advanced sensors. This fusion enables efficient data acquisition from above. The system’s mobility and precision are its core strengths.
Central to a LiDAR drone is the LiDAR sensor. It emits laser pulses that measure distances to objects below. This precise data is essential for accurate mapping and analysis.
Key elements of a LiDAR drone system include:
Drone Platform: Provides mobility and mission points.
LiDAR Sensor: Captures high-resolution distance data.
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU): Assesses motion and orientation.
Data Processing Software: Analyses captured data for generating valuable insights.
These elements work together seamlessly. Their integration ensures that LiDAR drones offer robust performance in diverse environments. From urban landscapes to rugged terrains, these drones deliver unmatched accuracy and efficiency.
The Rise of LiDAR Drones Survey in Industry and its benefits:
The adoption of drones across various industries is transforming traditional workflows, paving the way for greater automation and precision. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the value these technologies bring to their operations.

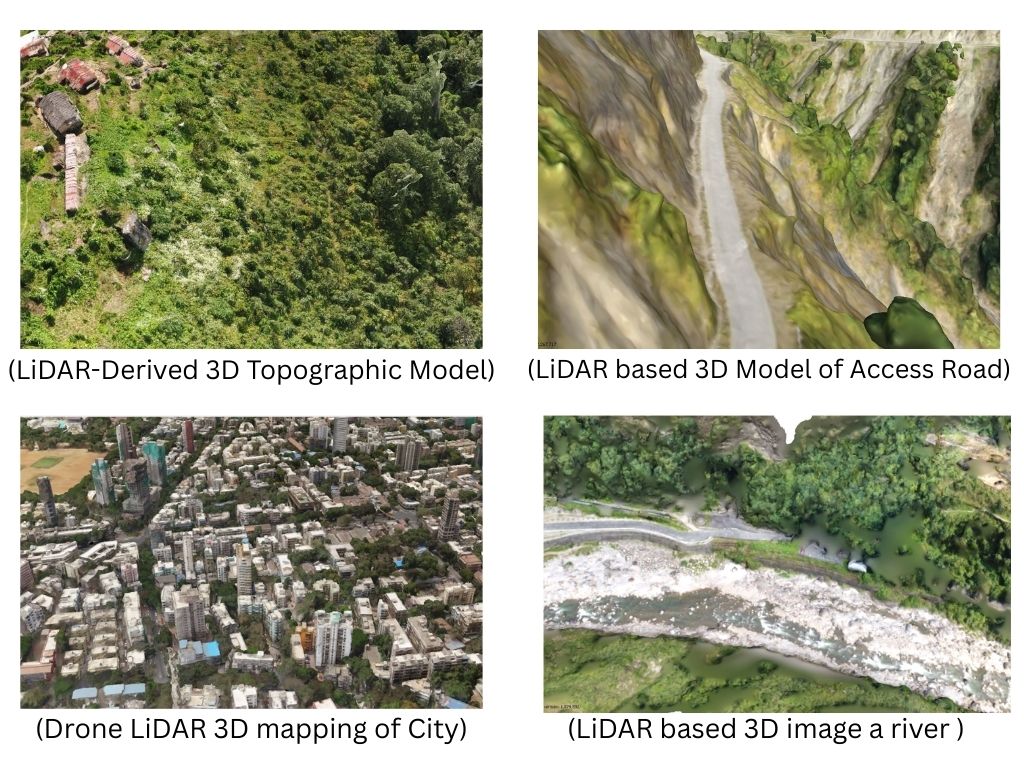
One of the driving forces behind this growth is the steady drop in drone costs. As technology becomes more affordable, its accessibility improves, encouraging organizations in multiple sectors to integrate drones into their processes.
Market insights point to a strong upward trajectory for the drone industry. Demand is surging as companies leverage drones for improved data gathering, better decision-making, and higher efficiency.
Prominent adoption trends include:
- Agriculture: Precision farming techniques and real-time crop monitoring.
- Construction: Accurate site mapping and streamlined project oversight.
- Forestry: Tracking environmental changes and managing natural resources.
- Mining: Conducting safety checks and detailed terrain assessments.
As these patterns evolve, drones are set to become an indispensable part of industrial operations. Their adaptability, combined with cost efficiency, makes them a game-changing asset for modern businesses.
Benefit of LiDAR Drone survey Across Key Industries
LiDAR drones are redefining the way industries operate, offering unmatched efficiency and precision. Their ability to capture accurate, real-time spatial data has unlocked significant economic and operational advantages across multiple sectors.
By replacing time-consuming manual processes with automated aerial data collection, these drones reduce costs, improve safety, and accelerate decision-making—transforming industry standards from agriculture to mining.
Agriculture: Precision for Higher Yields
In agriculture, LiDAR drones are driving a new era of precision farming. Farmers can now assess crop health with exceptional accuracy, enabling better resource allocation and higher productivity.
From monitoring water requirements to identifying early signs of pest infestations, the technology supports informed decisions while minimising waste. This targeted approach ensures sustainable farming without compromising yield.
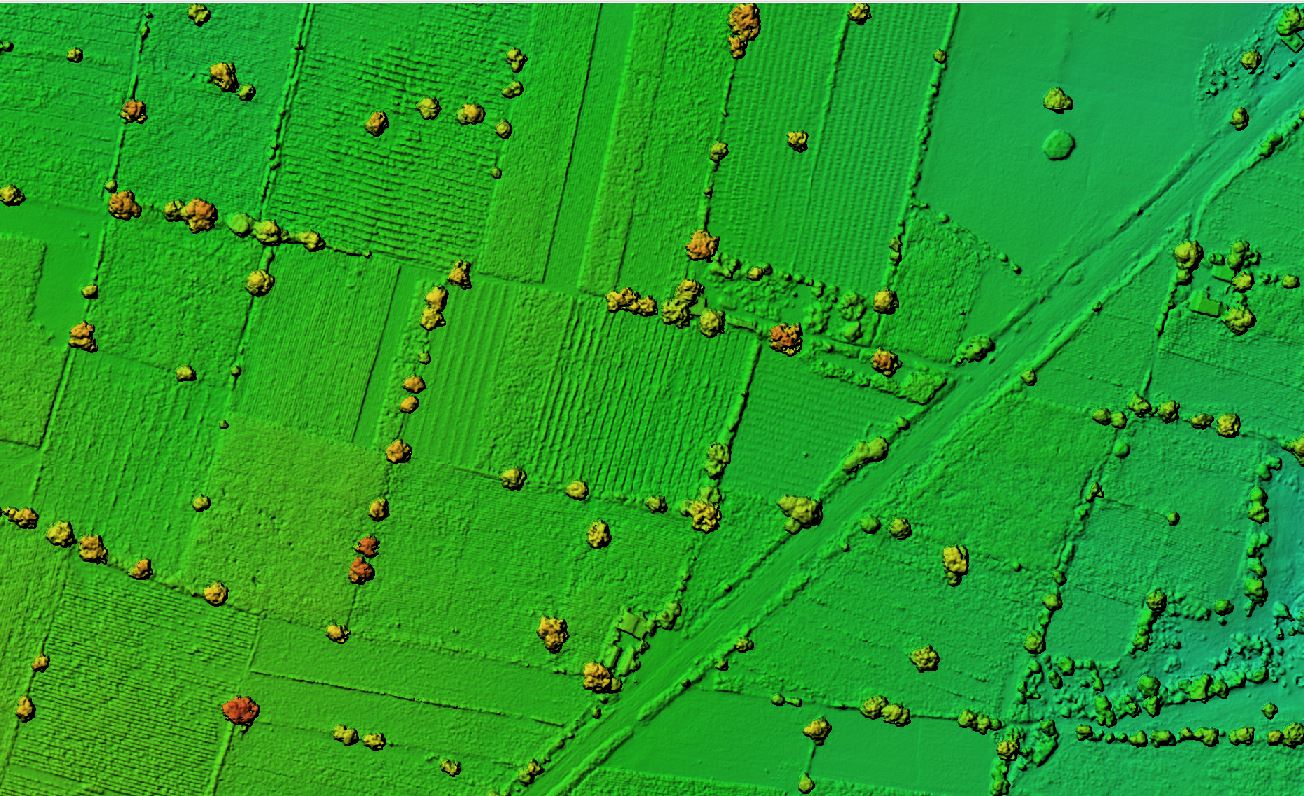
Key agricultural advantages:
- Highly accurate crop health monitoring.
- Optimised irrigation management
- Efficient pest and disease control
Construction & Infrastructure: Speed and Cost Efficiency
The construction sector benefits immensely from LiDAR’s speed and accuracy. Detailed site surveys that once took days can now be completed within hours, significantly reducing delays and budget overruns.
With precise progress tracking and enhanced resource allocation, project timelines are easier to maintain, ensuring smoother operations from planning to execution.

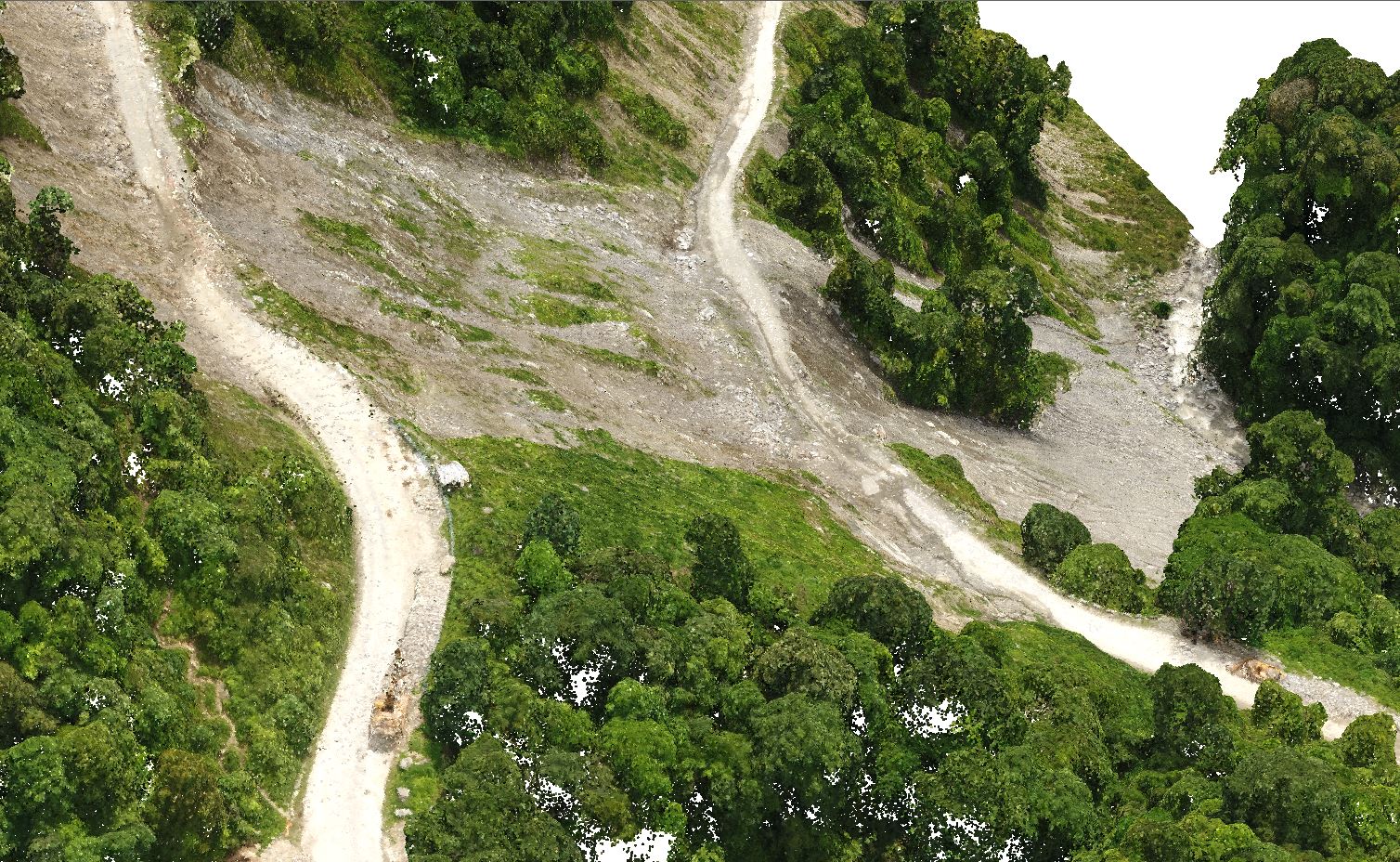
Construction benefits include:
- Rapid and detailed site mapping.
- Real-time progress and resource tracking.
- Reduced delays and improved budget control.
Forestry & Environmental Management: Data-Driven Sustainability
LiDAR drones are revolutionising forestry and environmental conservation by enabling accurate forest mapping and data analysis. These insights help in managing resources sustainably and protecting biodiversity.
From tree inventory to biomass estimation, drones provide information essential for conservation efforts while minimising the need for human presence in remote or hazardous environments.
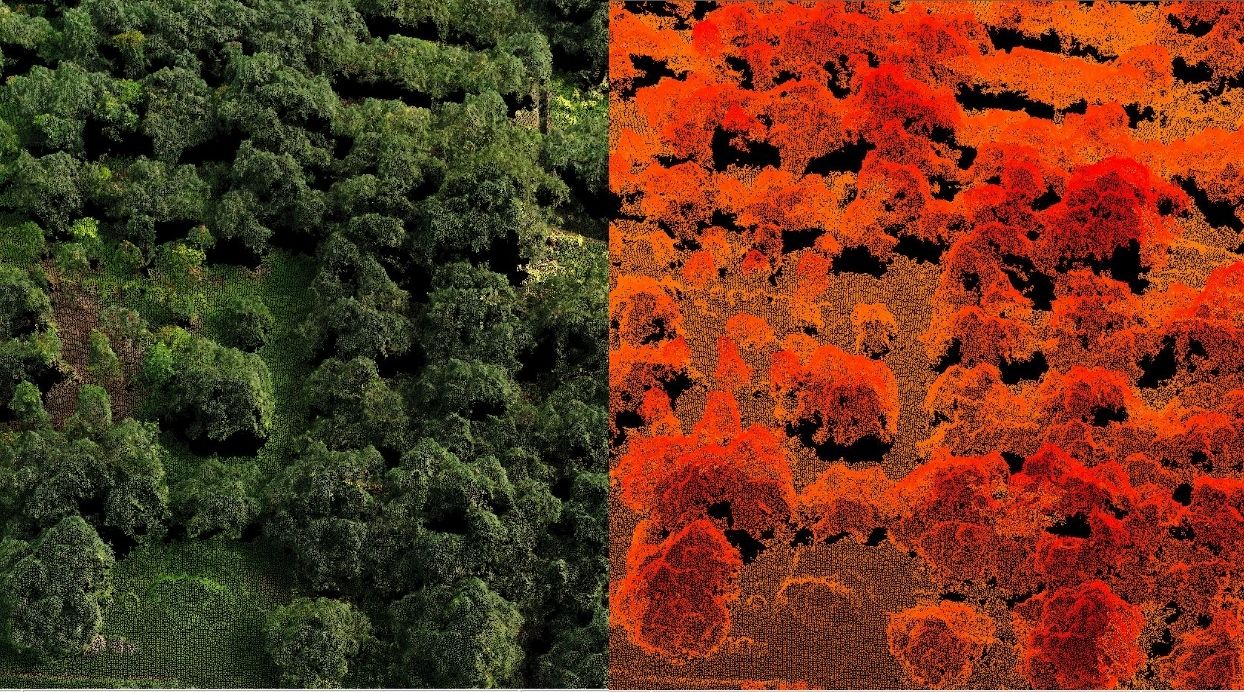

Forestry advantages:
- Comprehensive tree inventory and mapping.
- Accurate biomass calculations.
- Enhanced habitat mapping for conservation.
Mining & Resource Extraction: Safety and Strategic Insight
In mining operations, LiDAR drones offer a safer, more efficient way to collect vital data. Topographic and volumetric mapping is performed without sending workers into dangerous zones, reducing risk while improving accuracy.
The data enables better resource allocation, optimised extraction planning, and reduced operational costs.
Mining benefits:
- Precise topography and volume measurements.
- Reduced human exposure to hazardous areas.
- Improved operational planning.
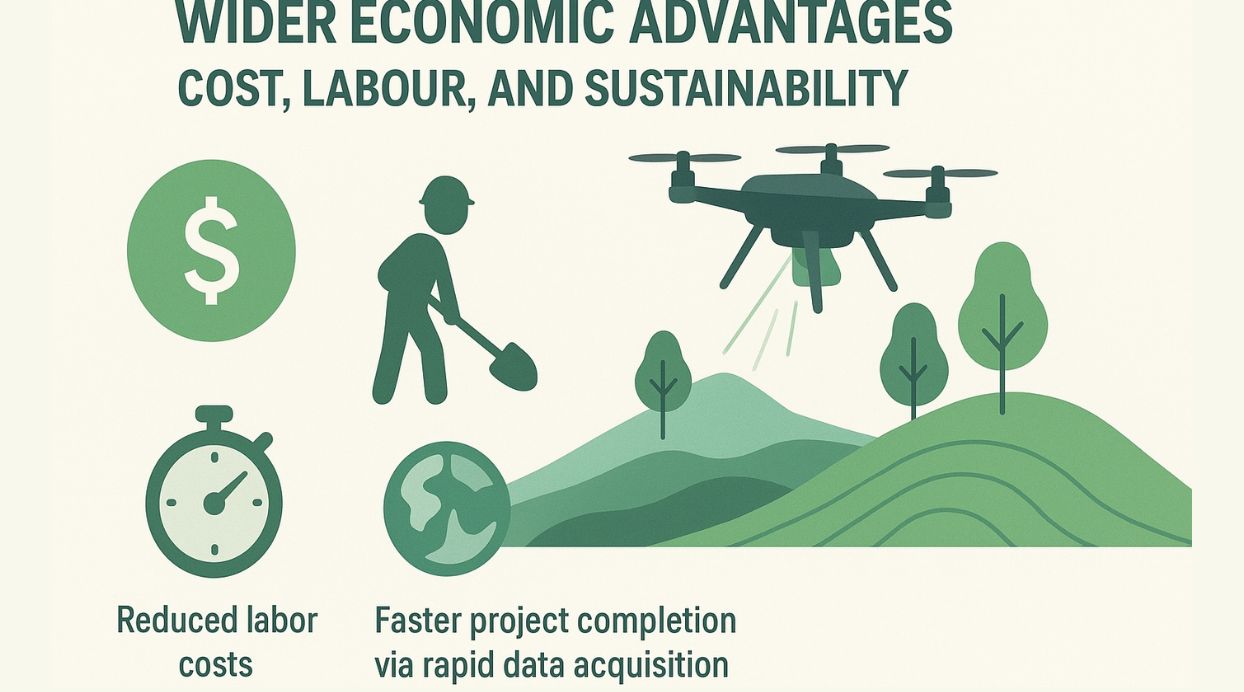
Wider Economic Benefit of LiDAR drone survey: Cost, Labour, and Sustainability
Beyond individual sectors, LiDAR drones deliver substantial economic value across industries. By reducing reliance on large field teams, companies save on labour expenses while maintaining high accuracy.
The ability to collect and process data faster shortens project cycles, enabling businesses to act more quickly on insights. Moreover, their low environmental footprint aligns with sustainable business practices, helping organisations meet regulatory and social responsibility goals.
Broader benefits:
- Lower operational costs through reduced manpower.
- Faster project completion via rapid data acquisition.
- Environmentally friendly operations with minimal disruption.
Challenges and Limitations of LiDAR Drones
Despite their benefits, LiDAR drones face several challenges. High initial investment costs can deter smaller companies from adopting this technology. Moreover, the need for specialised skills to operate and interpret data is a barrier for many businesses. This often requires additional training or hiring skilled personnel.
In terms of limitations, LiDAR drones may encounter difficulties in certain environments. Dense foliage or reflective surfaces can impede accurate data collection. Additionally, regulatory restrictions surrounding drone operations can limit their deployment in some regions.
Notable challenges include:
High initial costs.
Need for specialised skills.
Operational limitations in certain conditions.
These factors can affect the widespread adoption and effectiveness of LiDAR drone technology. However, ongoing advancements aim to overcome these hurdles, broadening their appeal across industries.
Future Outlook: Innovations and Expanding Applications
The future of LiDAR drones promises considerable growth and innovation. As technology advances, sensors become smaller, more affordable, and highly accurate. These enhancements open doors for new applications across various sectors, boosting their versatility.
Emerging applications include urban planning and autonomous vehicle development. LiDAR drones enhance mapping accuracy, crucial for constructing smart cities and safe autonomous transportation. Real-time data enables more responsive and efficient urban management strategies.
Promising areas of expansion comprise:
Urban planning.
Smart city development.
Autonomous vehicles.
Additionally, as integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning progresses, LiDAR drones will deliver more benefits in survey. This synergy can foster smarter decision-making, further transforming industries and societies alike. The continued evolution of this technology will undoubtedly redefine possibilities in the coming years.
Conclusion: The Transformative Power of LiDAR Drones
LiDAR drones are reshaping modern industries with their unmatched precision and efficiency. By reducing costs and enhancing productivity, they drive significant economic impacts. These drones serve as catalysts for innovation, integrating seamlessly into various applications from agriculture to urban planning.
As technology evolves, the potential for LiDAR drones will expand, offering even more sophisticated capabilities. Their role in enabling smart, data-driven practices is set to grow. LiDAR drones truly represent a transformative force, revolutionising how industries operate and thrive in our increasingly complex world.