LiDAR-equipped drones are reshaping data collection with unmatched accuracy and speed. By pairing high-resolution laser scanning technology with the mobility of drones, industries can now capture environmental information with a precision that was previously impossible.
The fusion of LiDAR with aerial platforms is revolutionizing remote sensing. From agriculture to construction to mining, organizations use it for detailed mapping, terrain analysis, and monitoring. As hardware costs drop and performance improves, LiDAR drones are becoming more accessible to both large enterprises and smaller operators.
Beyond industrial use, LiDAR plays a key role in autonomous vehicle navigation, enabling safe and accurate environmental awareness. Compact, affordable LiDAR solutions are expanding into new markets, while emergency response teams are using them to quickly assess disaster sites and plan interventions.
What LiDAR Is — and Why It Works So Well with Drones
LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, works by firing rapid laser pulses toward a surface and measuring the time it takes for them to return. This produces a highly detailed 3D map of the target area.
When LiDAR is mounted on a drone, its capabilities multiply:
- Higher mobility — reach challenging or dangerous locations
- Greater coverage — scan large areas faster than ground crews
- Immediate insights — process data in real time

This integration is particularly valuable for sectors like infrastructure development, forestry, and environmental conservation, where accurate spatial data directly impacts planning and decision-making.
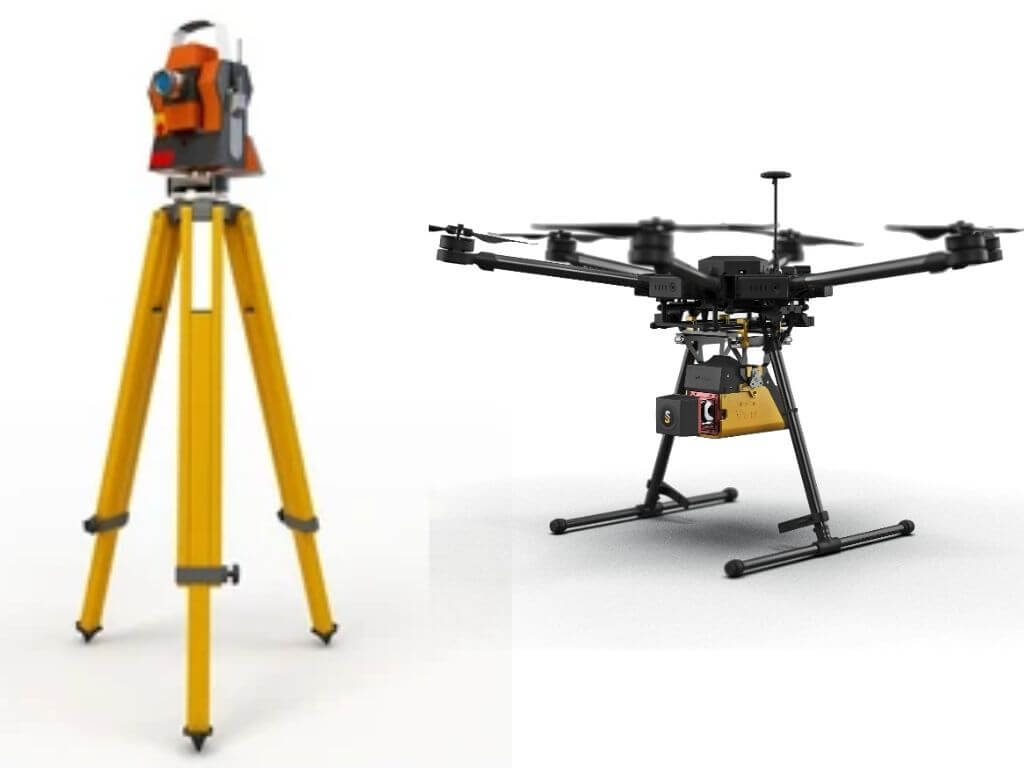
The Journey of LiDAR: From Tripods to UAVs
Early LiDAR systems were large, expensive, and used primarily for land-based surveying. Over time, miniaturization and cost reductions led to airborne LiDAR, first mounted on manned aircraft. This expanded coverage dramatically but still required significant operational budgets.
The latest leap puts LiDAR on drones, bringing:
• Lower operational costs compared to helicopters or planes
• Easier deployment in complex terrain
• Increased flexibility for repeated or on-demand surveys
This transition from ground to sky has expanded LiDAR’s reach, unlocking applications in industries that previously could not afford or access it.
How LiDAR Drones Capture Data
LiDAR drones fire rapid laser pulses toward the earth’s surface. By calculating the return time of each pulse, the system creates a 3D “point cloud” model of the landscape. Unlike cameras, LiDAR can penetrate tree canopies and map beneath vegetation, providing an accurate view of ground elevation and structures.
With drones:
• Aerial perspective allows comprehensive coverage
• Remote access enables mapping in difficult terrain
• Real-time feedback speeds up decision-making
These advantages make LiDAR drones indispensable in surveying, environmental monitoring, and resource management.
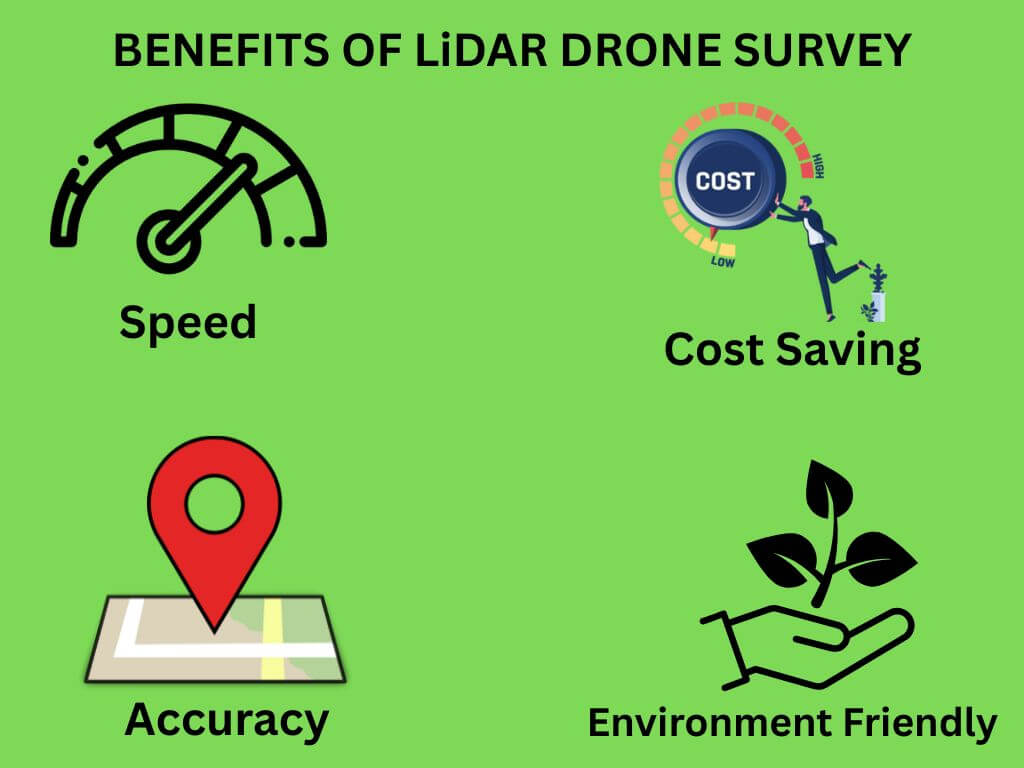
Benefits of LiDAR drone survey in Industries
LiDAR drones offer:
• Speed — cover more ground in less time
• Accuracy — highly detailed, precise measurements
• Cost savings — reduced manpower and equipment needs
• Environmental friendly — minimal on-site disturbance
Cities use them for urban planning, conservationists for habitat monitoring, and engineers for infrastructure inspection. Their adaptability ensures they fit seamlessly into multiple sectors.
Where LiDAR Drones Excel
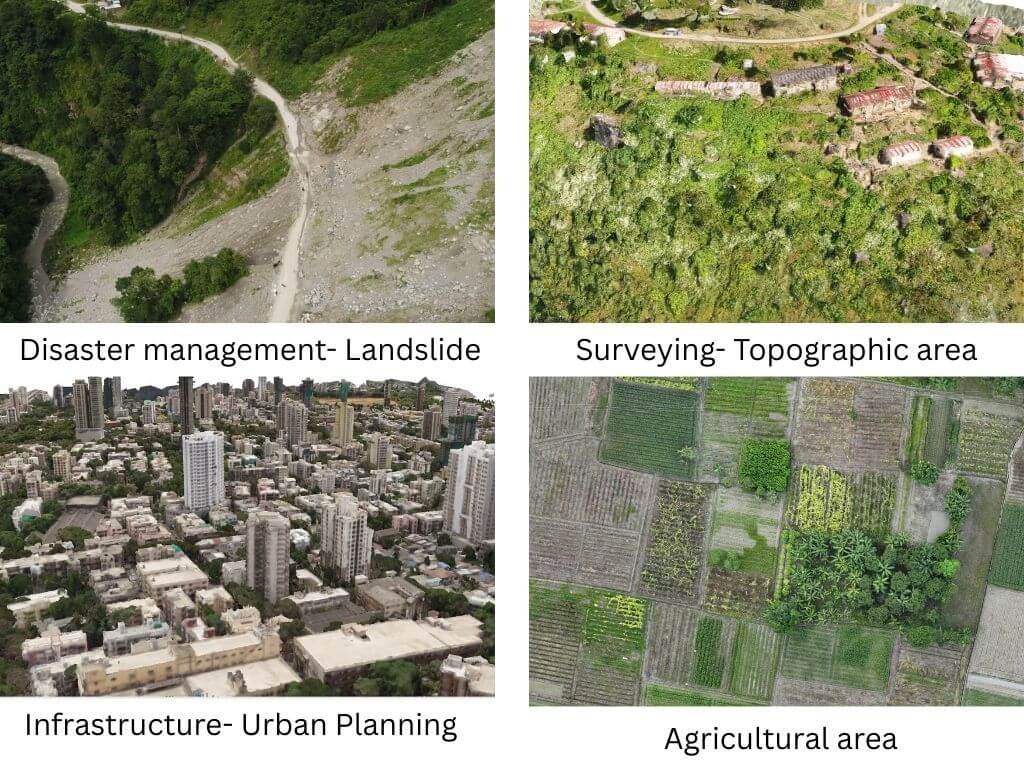
1. Surveying & Mapping – Produce detailed, accurate topographical data.
2. Construction & Infrastructure – Track project progress and verify designs.
3. Agriculture & Forestry – Assess crop health, forest density, and growth patterns.
4. Mining & Resource Management – Identify mineral deposits and monitor site changes.
5. Disaster Response – Quickly assess damage and plan relief operations.
Market Trends & Innovations in LiDAR drone precision mapping and industrial Surveying:
Current industry movements include:
• A shift toward smaller, more affordable LiDAR sensors
• Integration with artificial intelligence for automated data interpretation
• Increasing use by small-to-medium businesses
As AI advances, LiDAR data will become even more actionable, enabling predictive analysis and faster operational decisions.
Technological Advances Driving Growth
Recent breakthroughs include:
• Lightweight, high-resolution sensors suitable for small drones
• Faster, smarter software for processing massive datasets
• AI-powered analysis to detect patterns and anomalies automatically
These developments reduce costs, increase adoption, and broaden application possibilities.
Challenges to Consider
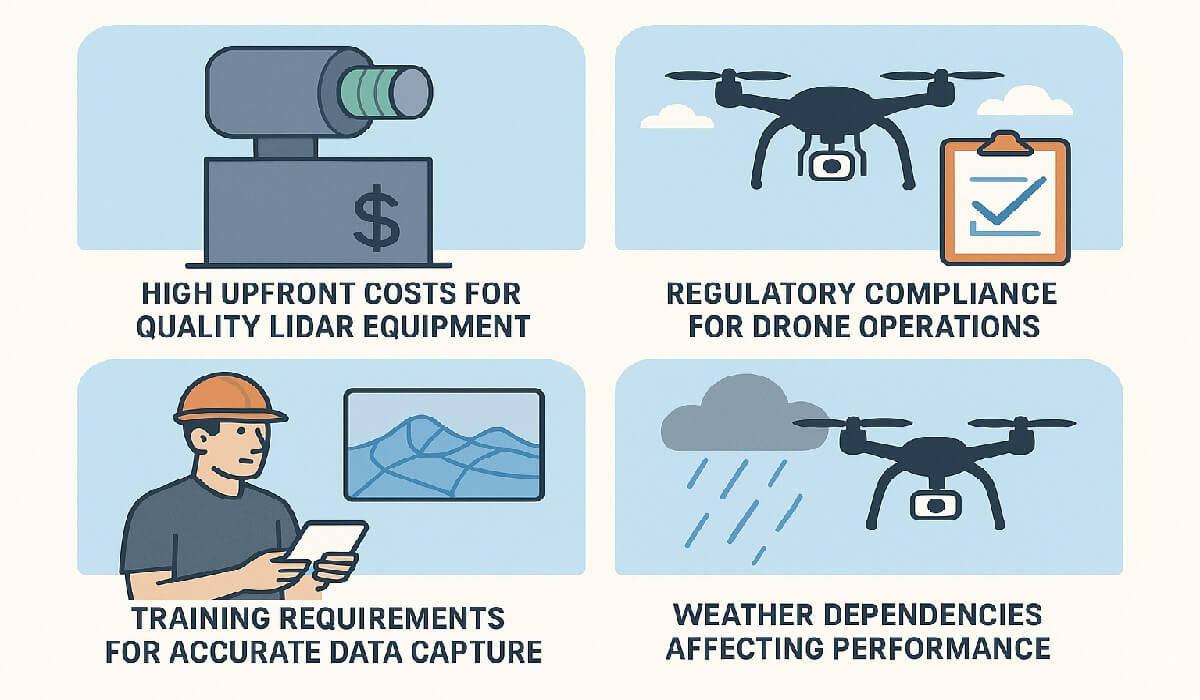
Adoption is not without obstacles:
• High upfront costs for quality LiDAR equipment
• Regulatory compliance for drone operations
• Training requirements for accurate data capture
• Weather dependencies affecting performance
Mitigating these requires careful planning, skilled operators, and adherence to local aviation laws.
Competitive Landscape
Major players like Hesai technology, RoboSense and Velodyne Lidar lead the market, but innovative startups are introducing niche solutions and budget-friendly models. This healthy competition drives technological innovation and affordability.
Looking Ahead: The Future of LiDAR Drones
In terms of LiDAR drone precision mapping and industrial survey
• Longer flight times with improved batteries
• Deeper AI integration for autonomous surveying
• Expansion into new sectors like archaeology and smart cities
As prices drop and performance rises, LiDAR drones will become a standard tool for organizations worldwide.
Conclusion
LiDAR drones are ushering in a new era of precision mapping and industrial survey. Their ability to gather rich spatial data quickly, safely, and cost-effectively makes them indispensable across a growing range of industries. The technology is moving from specialized use toward mainstream adoption — and those who embrace it now will be well-positioned for the data-driven future.

