LiDAR-equipped drones are revolutionising the way industries collect and use spatial data.
By combining aerial mobility with Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) Drones for Construction technology, these systems capture high-precision 3D information that powers applications from construction site mapping to wildlife conservation.
Mounted with advanced LiDAR sensors, these drones map the Earth’s surface in exceptional detail, generating accurate 3D models and supporting in-depth analysis. The result: greater efficiency, higher accuracy, and smarter decision-making across multiple sectors.
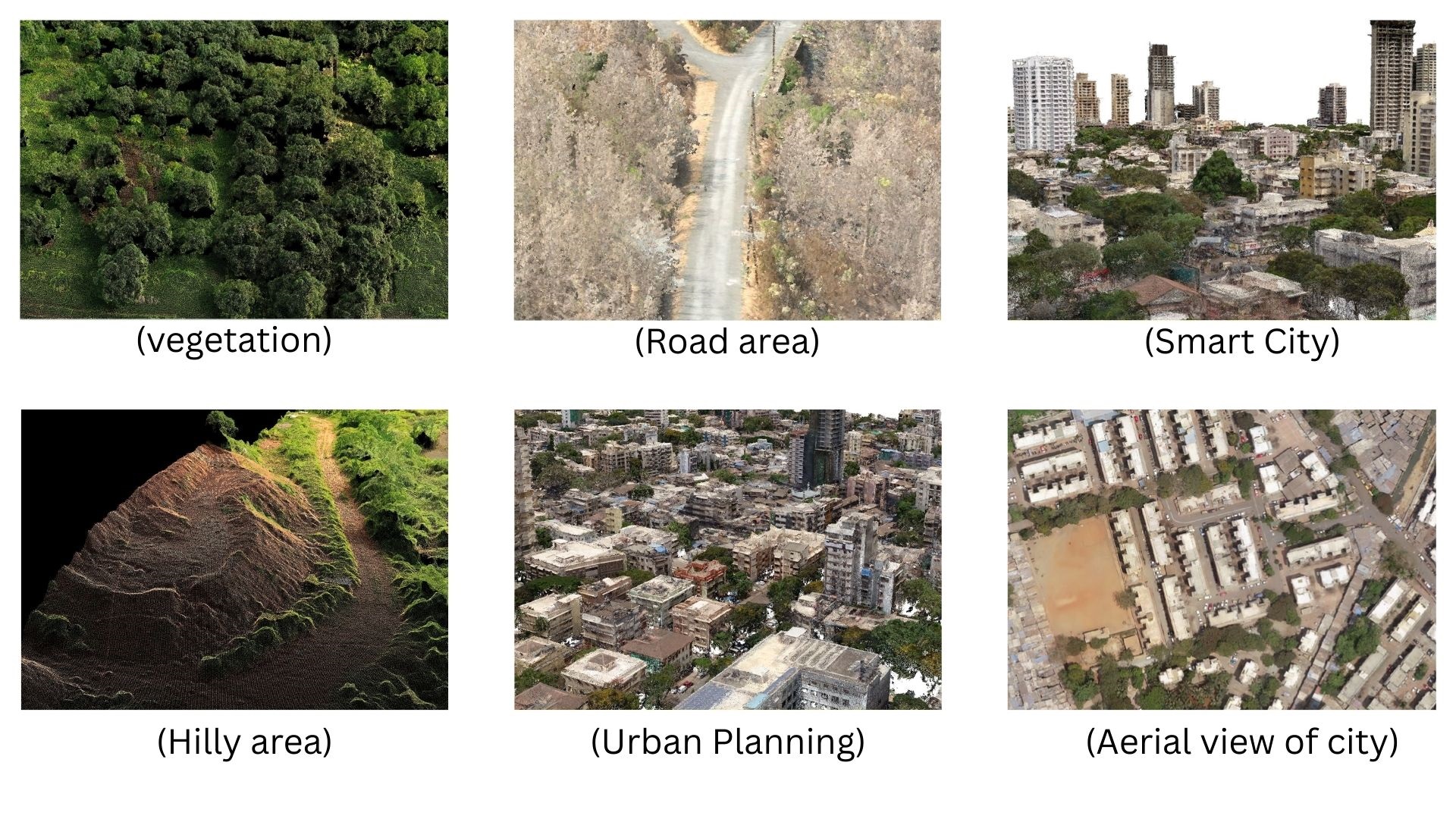
In construction, LiDAR drones produce exact topographical maps, streamlining site evaluation and project planning. In conservation, they help track environmental changes, assess vegetation health, and monitor wildlife habitats — essential for sustainable ecosystem management.
But their value doesn’t end there. From precision agriculture to urban planning, their capabilities are expanding as LiDAR technology evolves.

What is LiDAR? A Closer Look at the Technology
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) measures distances by sending out laser light pulses and recording the time it takes for them to return. This “time of flight” is converted into distance measurements, enabling the creation of detailed 3D terrain maps.
A typical LiDAR system includes:
Laser Scanner – Emits the laser pulses
GPS Receiver – Provides accurate positional data
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) – Maintains orientation accuracy
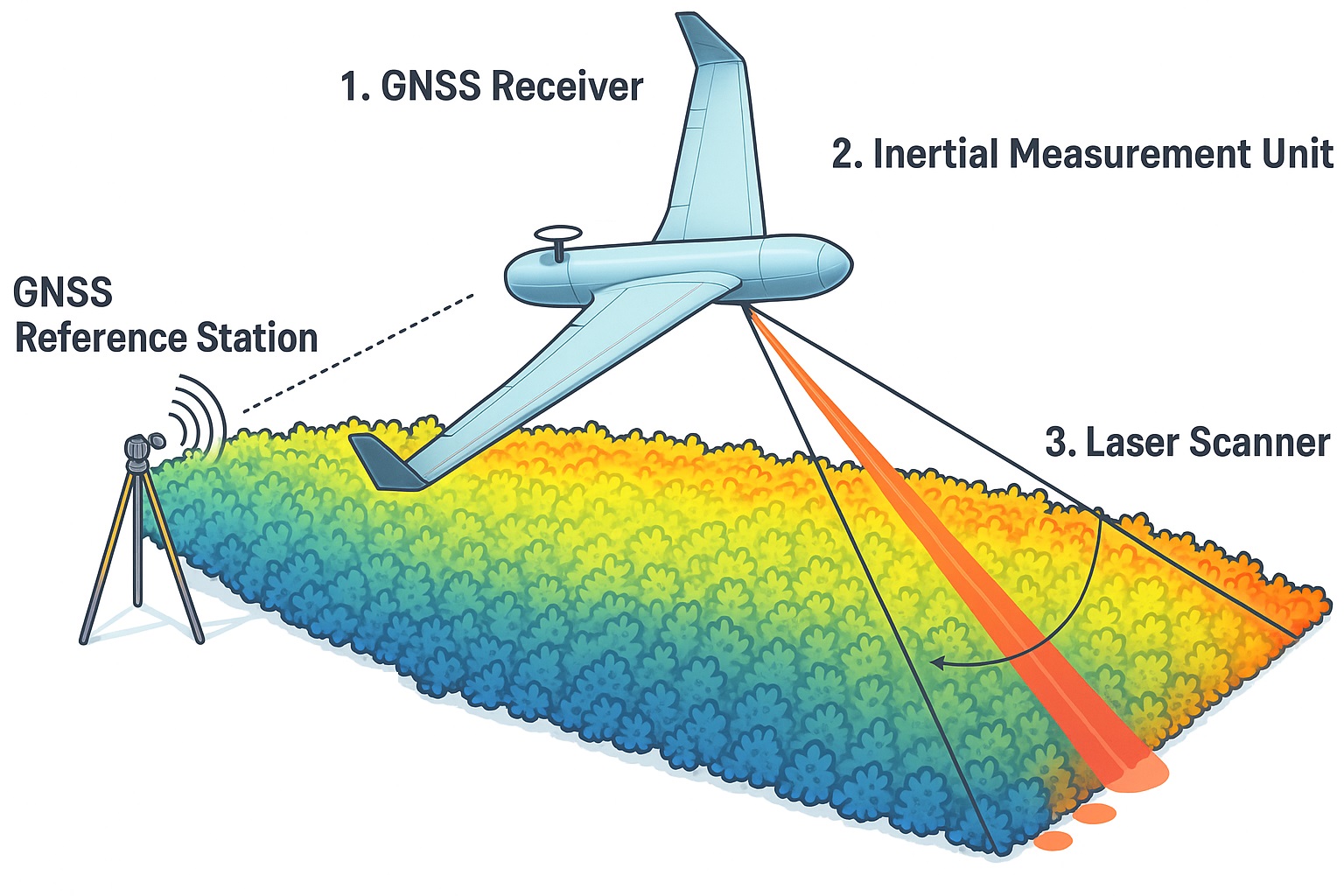
LiDAR works in varied environments, from dense forests to busy city streets. By detecting ground and surface features invisible to the naked eye, it delivers a reliable and unique perspective.
How LiDAR Drones Operate: Components & Workflow
LiDAR drones combine several high-tech components:
LiDAR Sensor – Fires thousands of pulses per second
GPS Module – Tracks precise location during flight
IMU – Ensures accurate orientation
Data Storage Unit – Saves collected data for processing
The process starts with precise flight planning to ensure full coverage. In flight, the drone scans the terrain, collecting millions of data points. After landing, specialised LiDAR processing software converts raw point clouds into usable 3D models for industry-specific applications.
LiDAR Drones vs Traditional Surveying & Photogrammetry
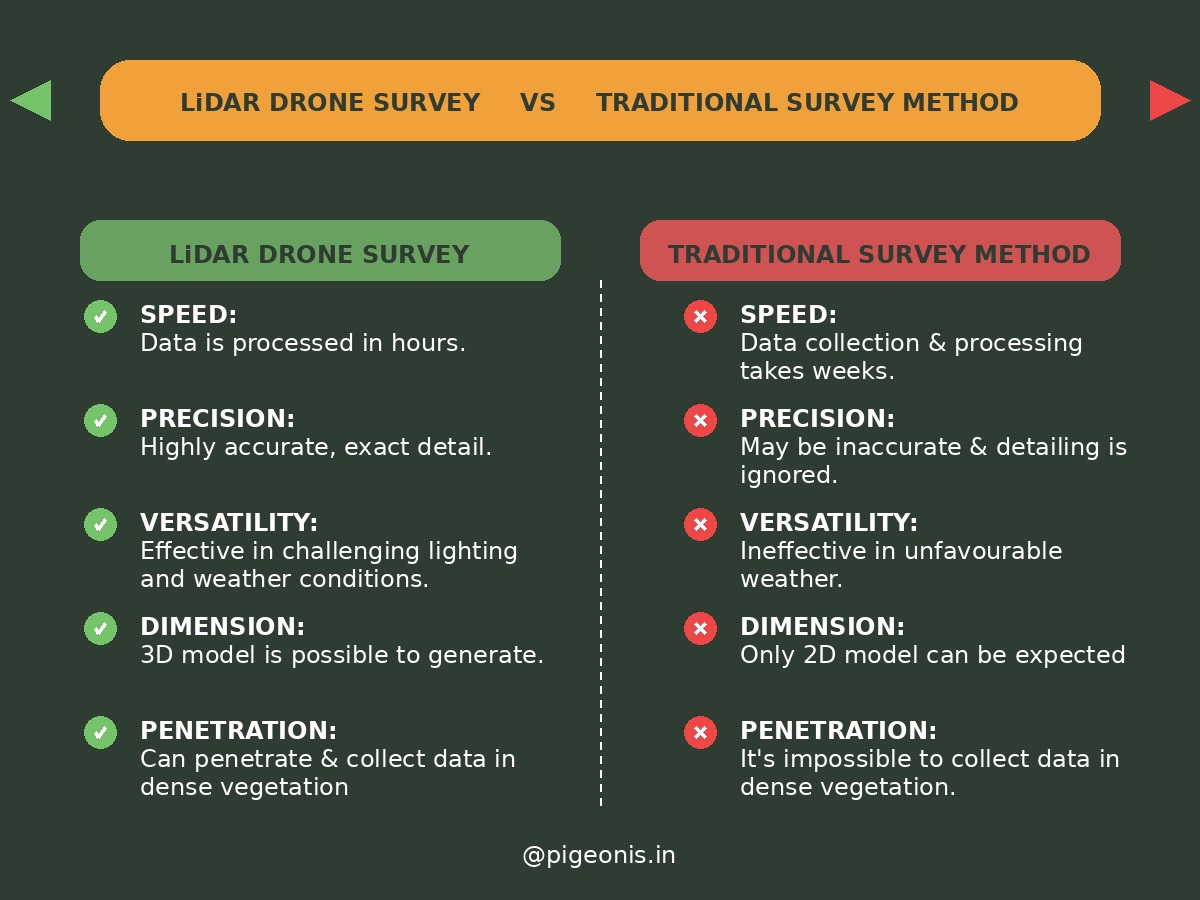
Compared to manual surveying or photogrammetry, LiDAR drones offer:
Speed – Surveys completed in minutes, not days
Precision – Centimetre-level accuracy
Versatility – Performs in low light, dense vegetation, and varied weather
Traditional surveying demands significant manpower and time, while photogrammetry struggles in poor lighting. LiDAR drones excel in challenging terrain with superior resolution.
Key Applications of LiDAR Drones
1. Construction & 3D Modelling
Reduced survey time and costs
Improved safety with fewer site visits
2. Conservation & Environmental Monitoring
Habitat mapping for biodiversity studies
Vegetation health analysis
Deforestation tracking without disturbing wildlife
3. Precision Agriculture
Irrigation mapping for efficient water usage
3D field models for crop planning
4. Forestry & Biomass Measurement
Canopy density mapping
Biomass and carbon storage estimation
Monitoring illegal logging activities
5. Mining & Volumetric Analysis
Stockpile volume calculation
Pit progress mapping
Environmental compliance checks
6. Urban Planning & Infrastructure Inspection
3D city modelling
Bridge, road, and railway inspection
Land use and zoning analysis
7. Archaeology & Cultural Heritage
Locating hidden sites under vegetation
High-detail structural documentation
Historical landscape reconstruction
8. Disaster Management & Emergency Response
Floodplain mapping and fault line detection
Post-disaster damage assessment
Targeted recovery and restoration planning
Inside a LiDAR Drone System: Sensors, Software & Processing
A LiDAR drone system typically includes:
LiDAR Sensor – Captures spatial data
Processing Software – Converts point clouds into actionable models
Power System – Sustains flight and sensor operation
Post-flight, advanced algorithms refine the data to ensure high accuracy for analysis.
LiDAR Drones for Construction: Benefits & Limitations
Advantages:
Extremely high accuracy
Rapid survey turnaround
Wide range of applications
Limitations:
Weather sensitivity
High initial investment
Requires trained operators
For most industries, the benefits far outweigh the limitations, especially where precision and efficiency are essential.
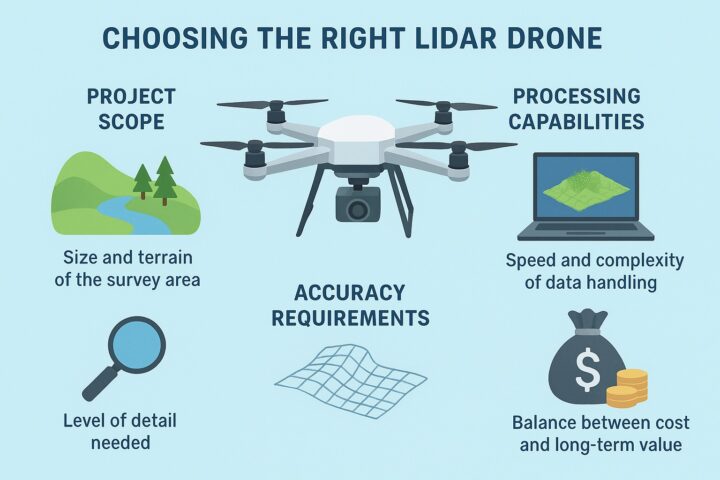
Choosing the Right LiDAR Drone
When selecting a LiDAR drone, consider:
Project scope – Area size and terrain complexity
Accuracy needs – Level of detail required
Processing capacity – Speed and capability of handling large datasets
Budget – Balancing initial cost with long-term ROI
The Future of LiDAR Drones
Upcoming developments include:
Miniaturised LiDAR sensors for lighter, more agile drones
AI-powered data analysis for automated insights
New applications in emerging sectors, even space exploration
LiDAR Drones in Construction or Conservation : Conclusion
From construction sites to conservation zones, LiDAR drones are now indispensable for accurate, efficient, and safe data collection. As costs drop and technology advances, adoption will accelerate — shaping the future of mapping, surveying, and spatial analysis.
With unmatched speed, precision, and versatility, LiDAR drones are set to remain at the forefront of industrial innovation.

One thought on “LiDAR Drones for Construction or Conservation: How LiDAR Drones Are Transforming Industries”